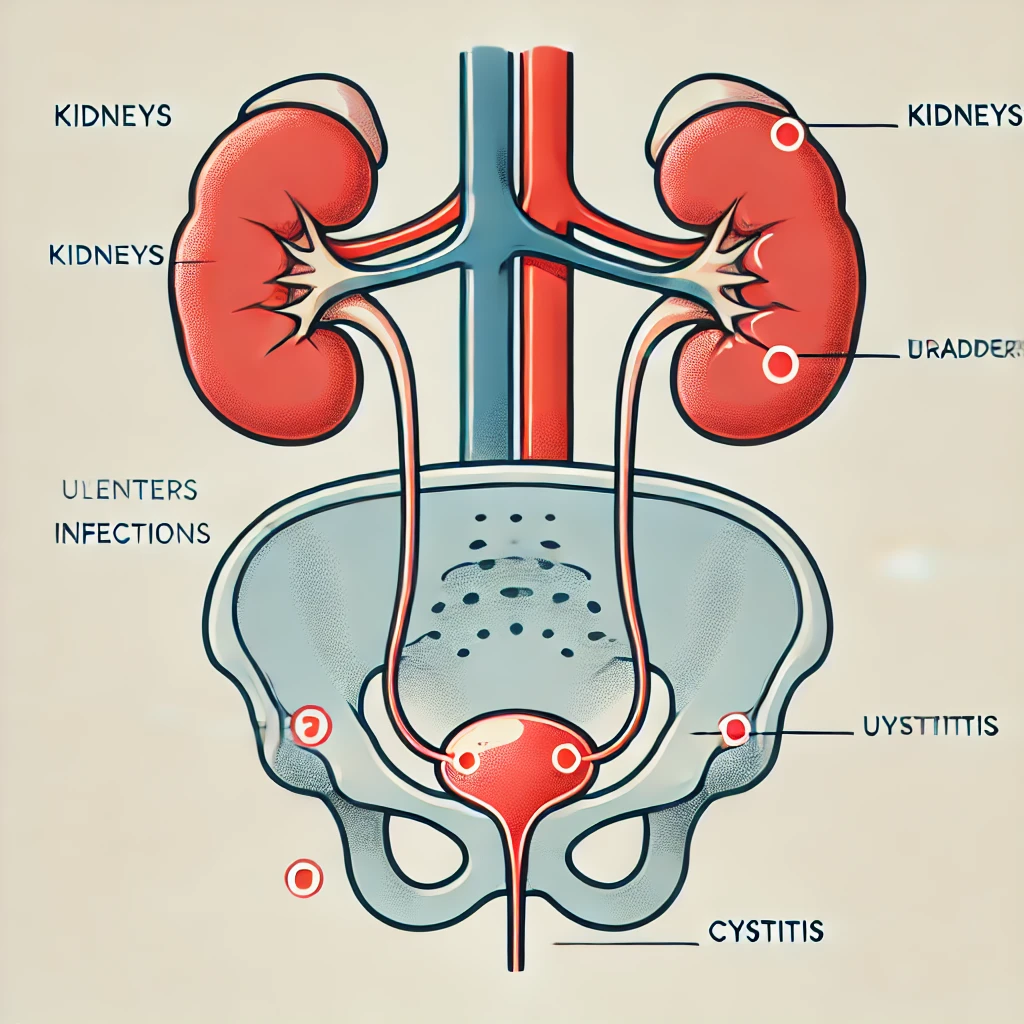
Understanding Urinary Tract Infection
urinary tract infection, Blood in urine after a UTI can sometimes occur. It is important to monitor whether the blood resolves after the infection clears up. Here is a summary of UTIs, including their symptoms,… Understanding Urinary Tract Infection