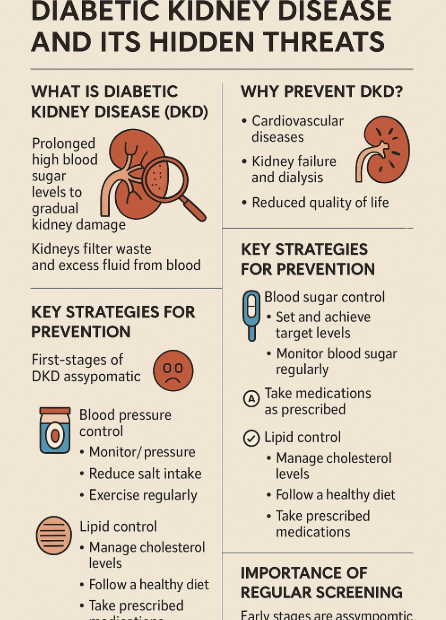
Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD): Is Prevention Really Possible? Your Complete Guide
Introduction: Diabetes and Its Hidden Threat, Diabetic Kidney Disease In today’s society, diabetes is no longer an unfamiliar disease. The widespread adoption of Westernized diets and sedentary lifestyles has led to a rapid increase in… Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD): Is Prevention Really Possible? Your Complete Guide