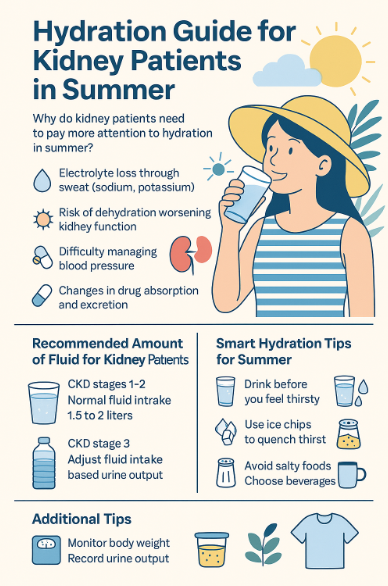
Summer Hydration for Kidney Patients: Your Comprehensive Guide to Staying Healthy
The scorching summer heat often sends us reaching for a refreshing glass of water to quench our thirst and cool down. However, for individuals living with kidney disease, drinking water is a far more delicate… Summer Hydration for Kidney Patients: Your Comprehensive Guide to Staying Healthy