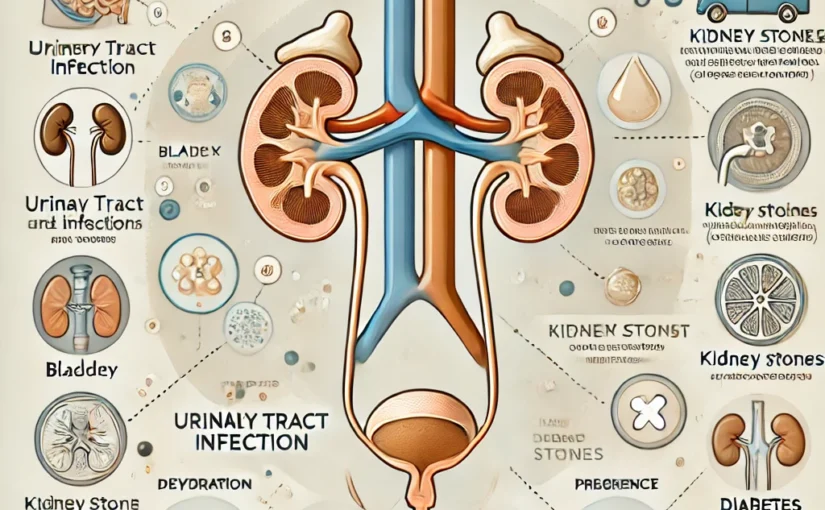
Have you ever noticed white sediment or particles in your urine? While it might be alarming, there are several potential causes—some of which are harmless, while others may indicate underlying health issues. Let’s explore the common reasons for white sediment in urine and when it’s time to seek medical advice.
What Are White Sediments in Urine?
White particles or sediments in urine can be a mixture of various substances, including:
- Microscopic cells (e.g., skin cells or blood cells)
- Mucus
- Proteins
- Minerals
In some cases, white sediments are normal and temporary. However, if the sediment is excessive or persistent, it may signal an underlying health condition.
Common Causes of White Sediments in Urine
-
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI), urine infection
- Bacterial infections in the urinary tract can cause inflammation and lead to the presence of white particles in it.
- Women may experience this with bladder infections or kidney infections, while men may develop prostatitis.
- Kidney Stones or Dehydration
- Mineral buildup, such as calcium or uric acid, can form sediments.
- Dehydration can also concentrate urine, causing minerals and other substances to precipitate.
- Vaginal Discharge (in Women)
- White discharge from the vagina may mix with urine and appear as sediment.
- Proteinuria (Excess Protein in Urine)
- Excess protein in the urine can make it appear cloudy or create white particles.
- This can be a sign of kidney dysfunction or other systemic conditions.
- Medications and Supplements
- Certain medications, such as antacids, can affect urine composition by increasing calcium concentration.
- SGLT2 inhibitors (a treatment for diabetes) may cause glucose excretion, potentially altering its composition.
- Diabetes
- High glucose levels can lead to glucose being excreted in the urine, which might appear as white sediment.
- Ketones from abnormal metabolism may also contribute to sediment in diabetic patients.
- Pregnancy
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy can increase vaginal discharge, which may mix with it and appear as sediment.
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI), urine infection
What Should You Do for good urine?
If you notice white sediments in your urine, consider these steps:
- Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water to help dilute it and flush out any unwanted substances. - Review Medications and Supplements:
Check if any medications or supplements you’re taking might be affecting. - Maintain a Balanced Diet:
Proper nutrition can help support your kidney and overall urinary health. - Consult a Doctor:
If the issue persists, seek medical advice. A test may help identify the cause and rule out any serious conditions.
When to See a Doctor
Persistent or excessive white sediments, especially when accompanied by symptoms such as pain, fever, or changes in urination, may require immediate medical attention. Common diagnostic steps include:
- Urinalysis: To detect infection, protein levels, or other abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: To assess kidney function and rule out systemic conditions.
White sediments can result from a variety of causes, ranging from dehydration and minor infections to more serious conditions like kidney dysfunction or diabetes. While many cases are harmless, persistent or unusual symptoms warrant medical consultation. Stay hydrated, maintain a balanced diet, and don’t hesitate to seek help when needed.