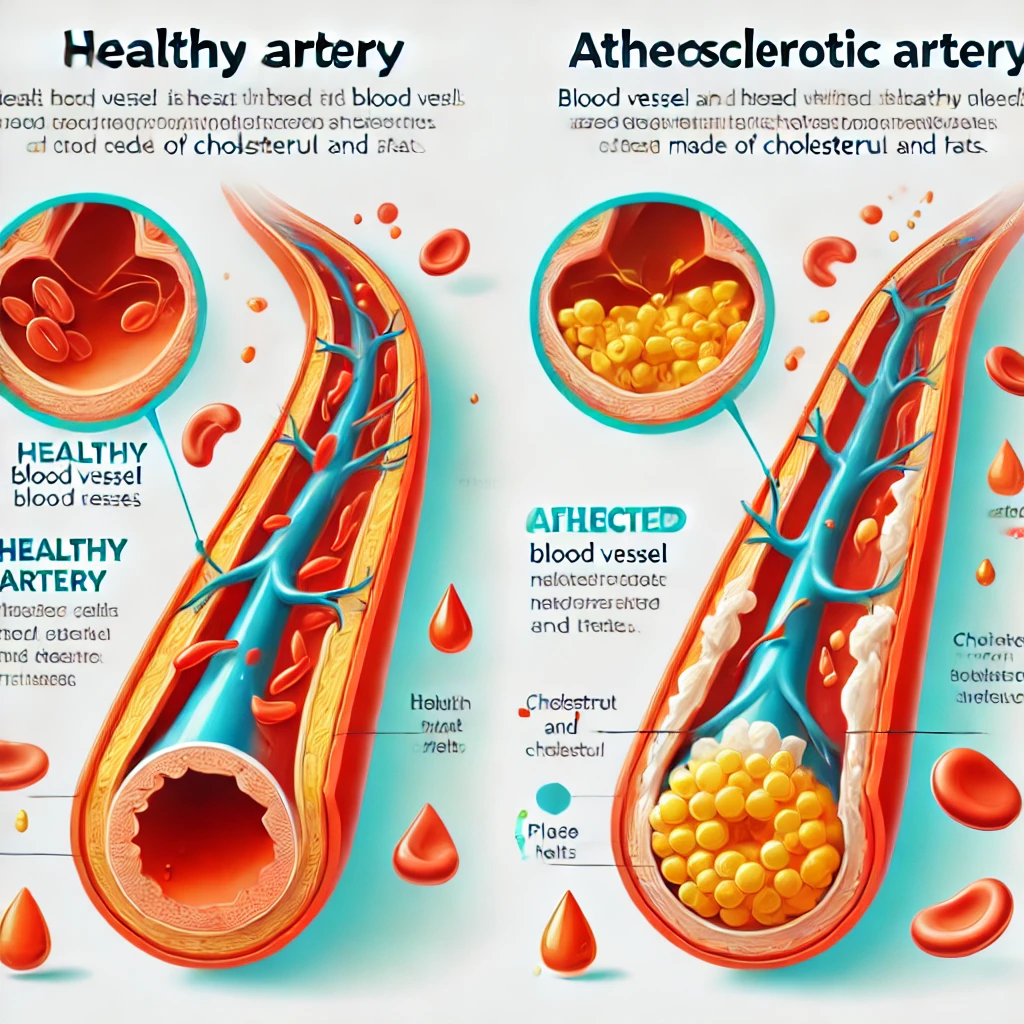
Atherosclerosis, I’m Afraid My Blood Vessels Might Get Clogged..
Atherosclerosis is one of the major health concerns for many people. Blocked blood vessels can lead to life-threatening conditions such as heart disease and stroke, making prevention and management crucial. In this post, we will… Atherosclerosis, I’m Afraid My Blood Vessels Might Get Clogged..