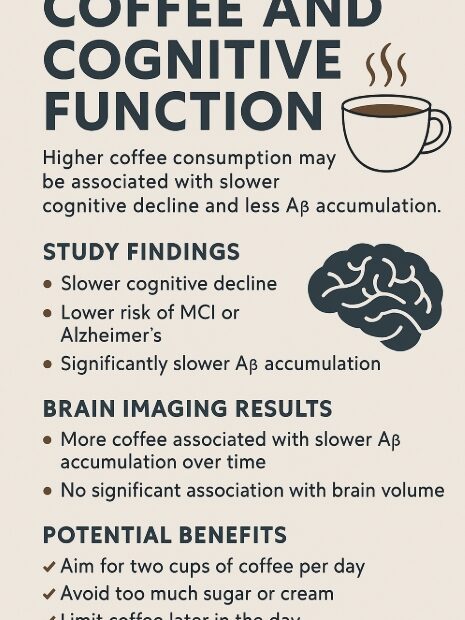
Should People with Kidney Disease Quit Coffee?
— A Coffee and Brain Health Guide for People with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Coffee is an irreplaceable part of modern life. A morning boost, an afternoon pick-me-up, a daily ritual. But what about people… Should People with Kidney Disease Quit Coffee?