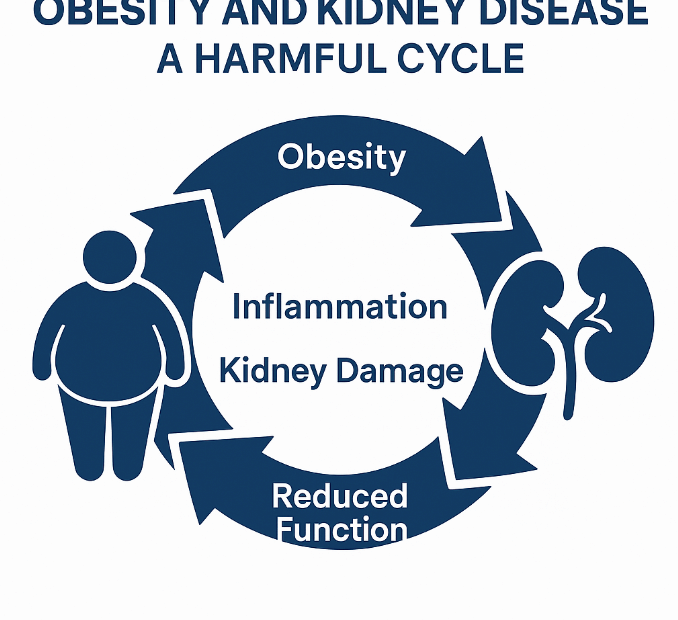
Do Kidney Disease Patients Need to Diet?
Many patients diagnosed with chronic kidney disease (CKD) ask the same question: “I don’t need to worry about weight anymore, right?”“Isn’t it dangerous for CKD patients to lose weight?” The answer isn’t simple. In short,… Do Kidney Disease Patients Need to Diet?