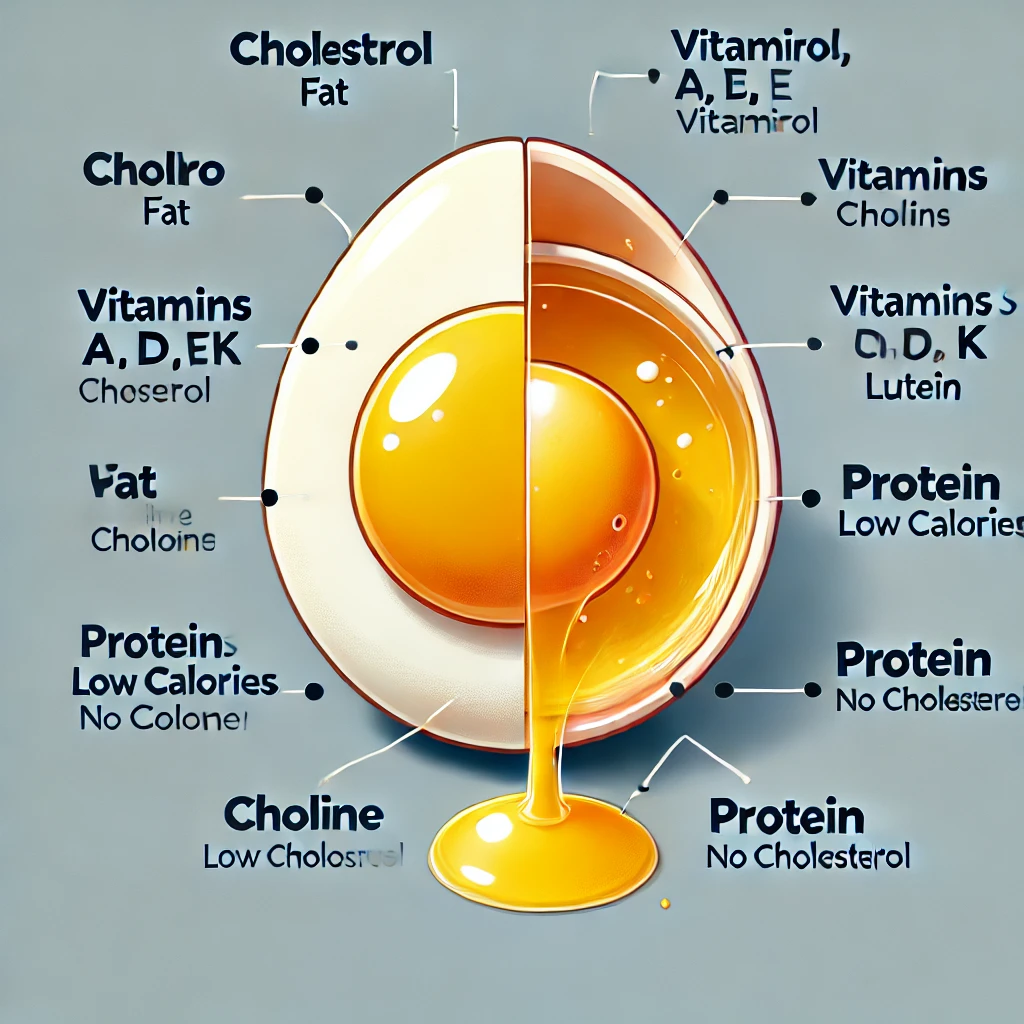
Is Egg Yolk Harmful and Egg White Beneficial?
1. Comparison of Egg Yolk and Egg White Nutrition Egg yolk, Eggs are a complete protein food that contains essential amino acids and various nutrients required by the body. However, a long-standing debate questions whether “egg… Is Egg Yolk Harmful and Egg White Beneficial?